BLOG ARTICLE
Amidst the recent surge in inflation rates across the globe, managing inflation risk has become vital for financial institutions in regions with historically low levels of inflation. In response to this increase in inflation, the Dutch Central Bank (DNB) compiled a list of 'Good Practices' for managing inflation risk, providing valuable insights for insurers and other financial institutions.
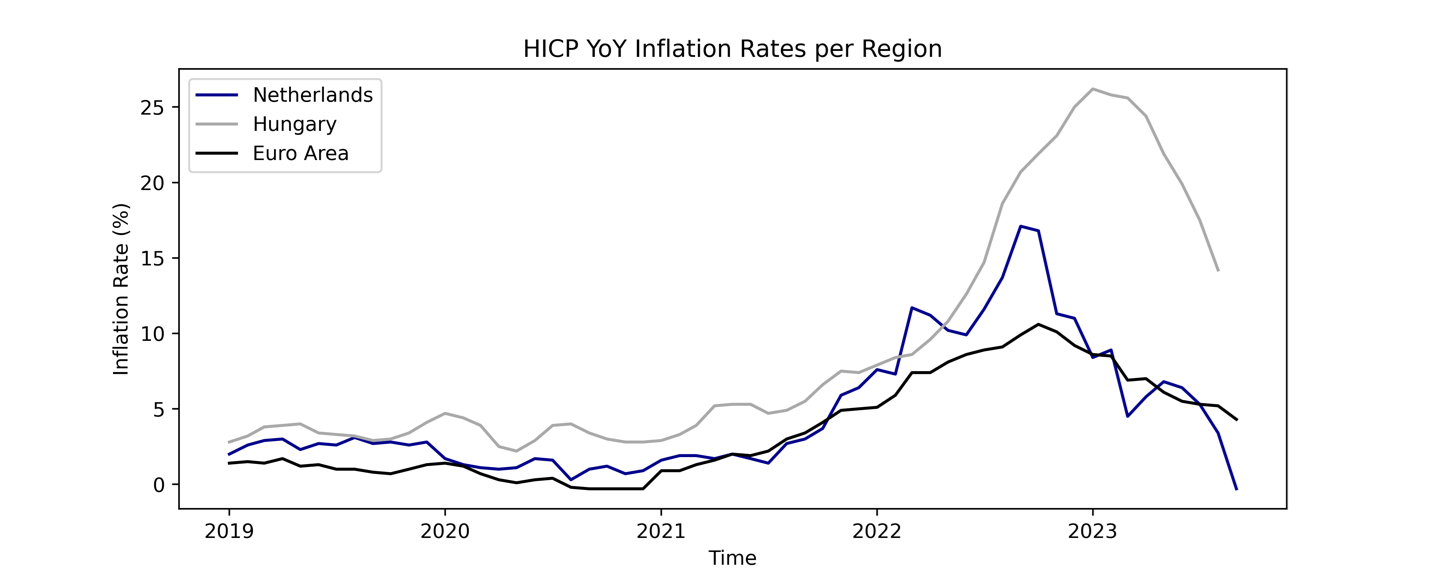
Figure: Graph comparing the YoY change of the Harmonized Indices of Consumer Prices (HICP) between the Netherlands, Hungary and Europe.
Inflation risk arises from unexpected increases in the cost of goods and services. If not hedged appropriately, these increases can negatively impact the ’balance sheet and consequently the solvency position of insurers. Inflation is influenced by a combination of various factors. These factors include expected inflation from wages and prices, as well as unexpected shock factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical conflicts.
DNB's recommendations, also known as 'Good Practices', are categorized into four key areas":
Risk Identification
Risk Policy, Tolerances and Limits
Inflation Assumptions
Business Operations
In terms of risk identification, insurers are encouraged to ensure that risks are analysed with a sufficient level of granularity. For insurance, different lines of business, sectors or geographical regions have nuances to the inflation it experiences. The goal is to ensure that insurers have a strong foundation upon which risk measurement, management and reporting can be conducted. They are also encouraged to include inflation risk in their risk policy, tolerances and limits. This includes setting an inflation risk tolerance, monitoring it with scenarios, defining early warning indicators and identifying potential management actions.
Given the importance of inflation assumptions, insurers are advised to use as much market-consistent information as possible. The methodology used should be documented and evaluated regularly, particularly when expert judgment is used to formulate inflation assumptions. In terms of business operations the guidance includes using hedging instruments, adapting the product development process and including inflation considerations in outsourcing policies.
Asset Liability Management (ALM) is also an important tool in managing inflation risk and insurers are encouraged to understand and manage mismatches that fall outside their risk tolerance. They should undertake hedging exercises to minimize this risk.
To conclude, DNB's 'Good Practices' provide a practical guide for insurers to manage and control their inflation risk. By implementing these strategies, insurers can better navigate the complexities of inflation risk and ensure their financial stability, especially in times of increased uncertainty.
This content has been first published on the website of Koninklijk Actuarieel Genootschap